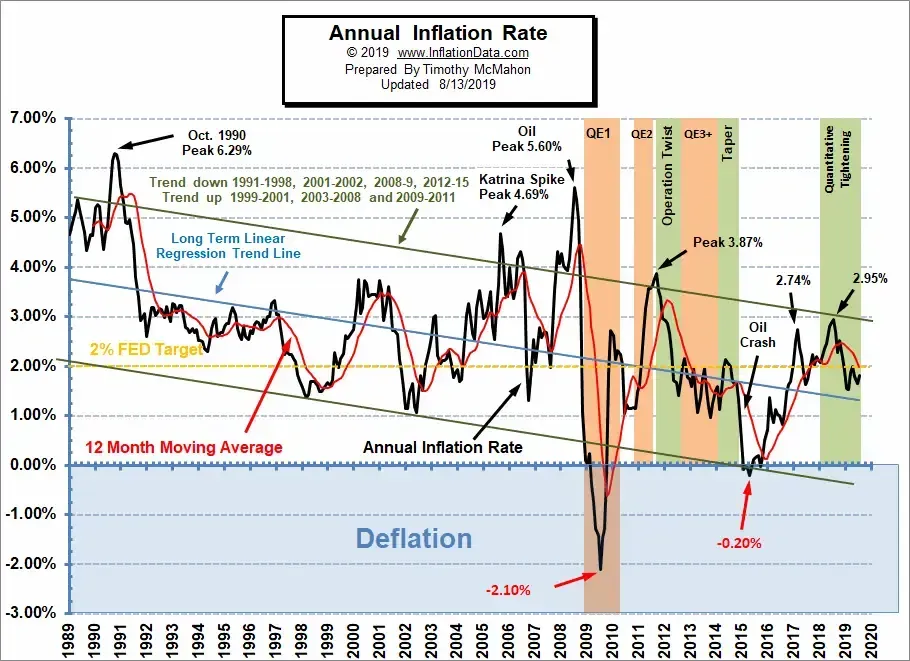
Inflation trends have become a focal point of economic discussions, particularly as the Federal Reserve navigates the complexities of rising prices. Recent data revealed that the PCE price index surged by 2.6% in December compared to the previous year, driven largely by increasing energy and food costs. This growth not only reflects consumer spending habits but also highlights the intricate relationship between inflation and interest rates. As core inflation stabilizes, understanding these inflation trends becomes crucial for predicting the broader economic outlook. With fluctuating prices impacting purchasing power, consumers and policymakers alike must remain vigilant in monitoring these indicators.
Exploring the dynamics of price increases, one can observe various inflationary pressures affecting the economy. The Personal Consumption Expenditures index, a vital measure of consumer price changes, has shown notable shifts, particularly in the context of consumer behavior and overall economic health. Factors such as rising consumer expenditures and changes in interest rates play significant roles in shaping these trends. Furthermore, core price measures exclude volatile categories like food and energy, allowing for a clearer view of underlying inflation patterns. As we delve deeper into these economic indicators, it becomes essential to comprehend their implications for future financial stability and growth.
Current Inflation Trends: An Overview
In December, the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index demonstrated a notable rise of 2.6% year-over-year, reflecting an escalating concern over inflation trends that have been persistent since the summer of 2022. This increase was driven primarily by surging energy and food prices, which have been volatile factors impacting consumer purchasing power. Economists had anticipated this rise, aligning their forecasts with the actual figures released by the Commerce Department, which indicated a month-to-month increase of 0.3%. This pattern highlights the ongoing challenges faced by consumers in an inflationary environment.
The stability of the core PCE price index, which excludes food and energy prices, is particularly noteworthy. Remaining steady at 2.8% annually over three months indicates that while overall inflation may be fluctuating, underlying inflation trends suggest some degree of control being exerted over price increases by the Federal Reserve. Such stability is crucial for formulating economic policy and providing insight into the broader economic outlook, influencing consumer spending patterns and interest rates.
Consumer Spending Patterns Amid Inflation
Despite rising inflation, consumer spending saw a significant increase in December, with a 0.7% rise surpassing economists’ expectations. This surge can be attributed to various factors, including the holiday shopping season and replacement purchases due to damages from recent hurricanes. The PCE price index’s insights into consumer behavior reveal that households are adapting their spending strategies in response to economic pressures, potentially increasing their expenditures on durable goods in anticipation of future price hikes.
However, the increase in consumer spending raises concerns about sustainability. As households face dwindling savings rates—falling to 3.8%—the reliance on credit cards has surged, indicating a shift in consumer sentiment. It suggests that while higher-income individuals continue to drive spending, those on the lower-to-middle end are becoming more cautious amid rising prices and interest rates. This disparity in consumer behavior will likely influence the economic outlook and monetary policy decisions moving forward.
Interest Rates and Inflation Control Strategies
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate policies play a critical role in managing inflation. As inflation rates remain elevated, the Fed has adopted a cautious approach, indicating that further rate cuts are not imminent. The robust labor market and strong economic indicators suggest that any adjustments to interest rates will be made judiciously, ensuring that inflation is kept in check while also supporting economic growth. The complexities of interest rate adjustments amid fluctuating inflation trends highlight the delicate balance the Fed must maintain.
Market reactions to inflation data and interest rate forecasts underscore the interconnectedness of these economic factors. Investors are closely monitoring the Fed’s next moves, especially in light of the recent inflation reports that indicate persistent pressures. Caution is advised as the economic landscape evolves, with potential policy changes that may arise from ongoing economic assessments and shifts in consumer behavior.
The Role of Core Inflation in Economic Forecasting
Core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, serves as a critical metric for understanding underlying inflation trends. The consistency of the core PCE price index at 2.8% provides a valuable perspective on the inflationary landscape, indicating that while overall inflation may fluctuate, core factors are stabilizing. This insight is vital for economists and policymakers as it helps shape the economic outlook and informs decisions regarding interest rates and monetary policy.
Tracking core inflation trends allows for a clearer picture of consumer price stability, which is essential for long-term economic forecasting. As the Federal Reserve aims for a 2% inflation target, understanding the nuances of core inflation helps gauge the effectiveness of current monetary policies. It also equips consumers and businesses with the knowledge needed to navigate the economic environment, influencing spending and investment decisions.
Economic Outlook: Challenges and Opportunities
The economic outlook remains uncertain, with inflation trends and consumer spending patterns presenting both challenges and opportunities. As inflation has cooled since its peak in 2022, the possibility of a soft landing—a scenario where price stability is achieved without triggering a recession—seems feasible. However, the potential implications of recent policy changes, such as tariffs and immigration restrictions, could introduce new complexities that may affect economic growth.
Furthermore, the balance between consumer spending and saving rates is critical for sustaining economic momentum. With a notable decline in the personal saving rate, consumers are increasingly dipping into their savings to maintain spending, which could lead to future financial strains. The interplay between these factors will be crucial for shaping the economic landscape in the coming months, necessitating careful monitoring by policymakers and stakeholders.
Disinflationary Forces at Play
While inflation pressures have remained significant, several disinflationary forces are beginning to take shape. Factors such as cautious consumer spending, limited pricing power among businesses, and substantial productivity growth are contributing to a broader trend of decreasing inflation rates. These elements suggest a potential easing of price pressures in the near term, providing some relief to consumers and the economy as a whole.
However, the path to sustained disinflation is fraught with uncertainty. The Federal Reserve’s cautious approach to monetary policy reflects the need for careful navigation through these complexities. As policymakers weigh the implications of tariffs and other regulatory changes, their decisions will be pivotal in determining the trajectory of inflation and economic stability moving forward.
Consumer Sentiment: The Diverging Trends
Consumer sentiment is showing signs of divergence, particularly between higher-income individuals and those with lower incomes. As inflationary pressures continue, it appears that higher-income households are more willing to maintain their spending levels, while lower-income consumers are becoming increasingly cautious. This split in sentiment poses potential risks to the overall economic recovery, as reliance on credit and reduced savings could hinder future spending.
Understanding these trends is vital for businesses and policymakers alike. As the economy evolves, tailored strategies will be necessary to address the needs of different consumer segments. By identifying the challenges faced by lower-income households, targeted support measures can be developed to ensure that all consumers can participate in and benefit from economic growth.
Future Inflation Risks: Navigating Uncertainties
Looking ahead, the risks of inflation remain a key concern for the economy. Various factors, including potential policy changes and the impact of tariffs, could lead to renewed inflationary pressures. As the Federal Reserve continues to monitor these developments, their ability to respond effectively will be crucial in maintaining price stability and supporting economic growth.
The dynamic nature of the economy necessitates a proactive approach to understanding inflation risks. By closely analyzing inflation trends and their underlying causes, stakeholders can better prepare for potential fluctuations in the economic landscape. This vigilance will be essential in navigating the challenges posed by inflation and ensuring a resilient economic future.
The Importance of Monitoring Economic Indicators
To effectively gauge the health of the economy, it is essential to monitor key economic indicators, including the PCE price index, consumer spending, and the personal saving rate. These metrics provide valuable insights into inflation trends and overall economic performance. By keeping a close eye on these indicators, businesses and policymakers can make informed decisions that align with the current economic landscape.
Furthermore, understanding the interplay between these indicators allows for a more comprehensive analysis of economic conditions. For instance, shifts in consumer spending habits may signal changes in inflationary pressures, prompting necessary adjustments in monetary policy. By staying attuned to these evolving dynamics, stakeholders can better navigate the complexities of the economic environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the recent trends in the PCE price index and how do they reflect inflation trends?
The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index has shown an increase, climbing 2.6% in December year-over-year, up from 2.4% in November. This indicates a continuing trend of inflation, particularly influenced by rising energy and food costs. However, the core PCE, which excludes volatile items, remains steady at 2.8%, suggesting some stability in underlying inflation trends.
How is consumer spending impacting inflation trends and economic outlook?
Consumer spending has surged by 0.7% in December, exceeding expectations. This increase indicates a robust economic outlook but also raises concerns about inflation trends, especially as consumers are relying more on credit and savings are dwindling. Such spending behaviors can lead to sustained inflationary pressures if not matched by income growth.
What role do interest rates play in current inflation trends?
Interest rates are a critical factor in managing inflation trends. The Federal Reserve is cautious about rate cuts due to persistent inflation. With inflation still high, maintaining higher interest rates can help cool down consumer spending and stabilize prices, aligning with the Fed’s long-term target of 2% inflation.
How does core inflation relate to overall inflation trends in the economy?
Core inflation, which excludes food and energy prices, provides a clearer picture of underlying inflation trends. The core PCE index remained at 2.8%, indicating stability despite fluctuations in overall prices. This suggests that while some inflationary pressures exist, they may not be as widespread as indicated by total inflation metrics.
What is the economic outlook regarding inflation trends for the upcoming months?
The economic outlook suggests that while inflation trends have shown some cooling since their peak in 2022, the journey toward the Federal Reserve’s 2% inflation target may be lengthy and uneven. Factors such as cautious consumer spending and potential impacts from new tariffs could influence future inflation rates.
How have consumer saving rates affected inflation trends in the current economic environment?
The decline in consumer saving rates, which fell to 3.8%, reflects a shift in consumer behavior amidst a high-price environment. Lower savings can lead to increased reliance on credit, potentially exacerbating inflation trends as consumers spend beyond their means, impacting overall economic stability.
What are the implications of rising energy and food prices on inflation trends?
Rising energy and food prices significantly influence overall inflation trends, as seen in the recent PCE price index data. These essential costs directly affect consumers’ purchasing power and can lead to broader inflationary pressures if they persist, challenging the Federal Reserve’s efforts to manage price stability.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Inflation Measure | The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index rose by 2.6% year-over-year in December, up from 2.4% in November. |
| Monthly Change | Prices increased by 0.3% month-to-month in December compared to a 0.1% rise in November. |
| Core PCE Index | Excluding food and energy, the core PCE index rose by 0.2% from November, maintaining a 2.8% annual rate. |
| Consumer Spending | Consumer spending increased by 0.7% in December, surpassing the 0.5% expected increase. |
| Savings Rate | The personal saving rate fell to 3.8%, the lowest in two years, indicating consumers are saving less. |
| Future Outlook | Disinflationary trends are expected to continue, but inflationary risks remain due to policy changes and tariffs. |
Summary
Inflation trends indicate a complex landscape as the Federal Reserve’s preferred measure shows a rise in December, primarily driven by energy and food prices. However, the core inflation metric suggests some stabilization in underlying price increases. As consumer spending remains strong but savings dwindle, the economic outlook reflects both progress and potential challenges ahead.